Rome Criteria for Irritable Bowel Syndrome Diagnosis
IBS is a physical - not psychological - disorder that affects mainly the bowel, and is characterized by lower abdominal pain (mild to severe, there is a spectrum), diarrhea, constipation (or alternating diarrhea/constipation), gas, bloating, and nausea.
(See what an IBS attack literally looks like.)
IBS is not a disease, it's a functional disorder, and it's actually characterized as a brain-gut dysfunction.
Because IBS is not a disease, but a condition wherein your gastrocolic reflex goes awry, diagnosis depends in part on determining whether or not your symptoms match those that have been medically established as definitive of Irritable Bowel Syndrome.
The Rome IV Criteria, last updated in 2016, are the current standard for this definition.
The Rome diagnostic criteria of Irritable Bowel Syndrome always presumes the absence of a structural or biochemical explanation for the symptoms and is made only by a physician.
Interview with Heather Van Vorous ~
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The Importance of Diagnosis
Irritable Bowel Syndrome can be diagnosed based on at least 1 day per week during the previous 3 months of lower abdominal pain in association with:
1. change in stool frequency and/or
2. change in stool form and/or
3. changes related to defecation
Symptoms that Cumulatively Support the Diagnosis of IBS:
1. Abnormal stool frequency (may be defined as greater than 3 bowel movements per day and less than 3 bowel movements per week);
2. Abnormal stool form (lumpy/hard or loose/watery stool);
3. Abnormal stool passage (straining, urgency, or feeling of incomplete evacuation);
4. Passage of mucus;
5. Bloating or feeling of abdominal distension.
Supportive Symptoms of IBS:
1. Fewer than three bowel movements a week
2. More than three bowel movements a day
3. Hard or lumpy stools
4. Loose (mushy) or watery stools
5. Straining during a bowel movement
6. Urgency (having to rush to have a bowel movement)
7. Feeling of incomplete bowel movement
8. Passing mucus (white material) during a bowel movement
9. Abdominal fullness, bloating, or swelling
Red Flag symptoms which are NOT typical of IBS:
Pain that often awakens/interferes with sleep
Diarrhea that often awakens/interferes with sleep
Blood in your stool (visible or occult)
Weight loss
Fever
Abnormal physical examination
IBS Subtypes - Rome Criteria Charts

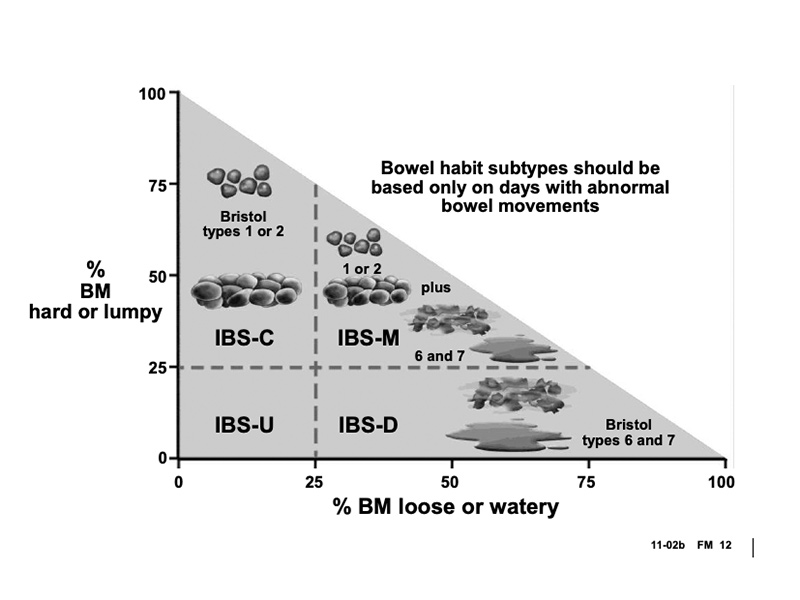

Once you have a firm IBS diagnosis, take heart. While there is no cure yet, there are many ways to successfully manage - and prevent - all IBS symptoms. You can control your IBS, not vice versa.
IBS Diet Cheat Sheet for All Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms
If you're confident that you've been properly diagnosed with IBS, there are several key IBS treatments for successfully managing symptoms:
* Follow the explicit IBS diet guidelines and IBS safe recipes
* Try the only possible cure for IBS, gut-directed hypnotherapy
* Inform yourself with the best-selling and best-reviewed IBS books available
* Find the most helpful IBS supplements for specific symptoms
* Come join our IBS community
